Healthcare Data Breaches Expose 560,000 Records: Strengthening Cybersecurity to Prevent Future Attacks

The recent breaches in healthcare exposed over 560,000 records, with data including Social Security numbers, medical records, and insurance details. Ransomware gangs like Rhysida and BianLian claimed responsibility for the attacks. These incidents highlight the need for better cybersecurity in healthcare.
This is an overview of several ransomware attacks, with healthcare being a frequent target. If you work in the healthcare sector, you’re likely aware of this.
In Maine, there’s a requirement to disclose data breaches involving state residents as part of regulatory obligations. When a breach is disclosed by the Maine Attorney General's office or the HHS Office for Civil Rights (OCR), they provide details on how many people were affected and what data was compromised. However, they won’t disclose how the breach occurred, as that's not required in the breach notification.
For example, a breach that occurred in July 2024, with the investigation only concluded in January 2025, left a 6-month gap. This means threat actors had six months to exploit personal data, and the affected individuals were unaware.
In some cases, organizations might extend investigations deliberately to delay public reporting, potentially prolonging the exposure of sensitive information.
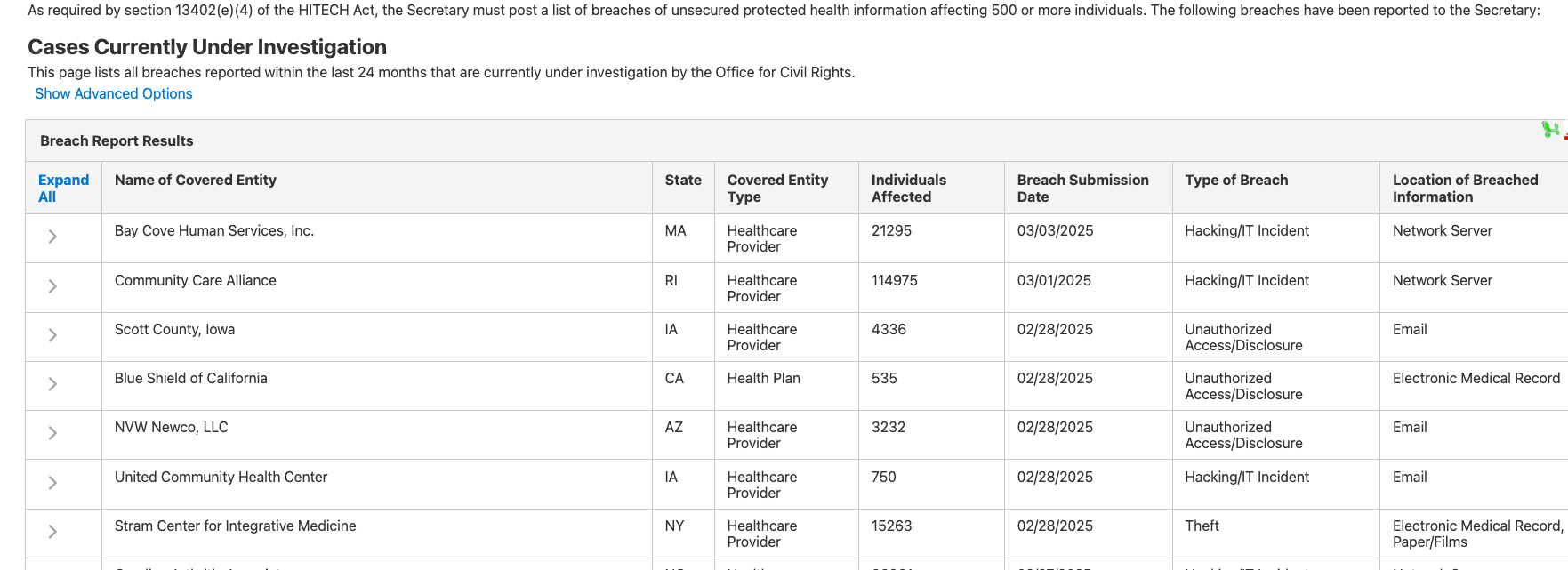
Follow this link to view Cases Currently Under Investigation :
https://ocrportal.hhs.gov/ocr/breach/breach_report.jsf
Prevention Guidelines:
- Encrypt Data: Ensure all sensitive data is encrypted, both in storage and during transit.
- Strengthen Access Control: Implement strict, role-based access and multi-factor authentication (MFA) for sensitive systems.
- Regular Security Audits: Conduct regular vulnerability assessments and patch management to identify and fix weaknesses.
- Employee Training: Train staff on cybersecurity best practices and how to spot phishing or social engineering attempts.
- Incident Response Plan: Have a clear, tested incident response plan for fast action during breaches.
- Data Backup: Regularly back up data and ensure backups are isolated from the main network.
- Monitor for Anomalies: Use network monitoring and anomaly detection tools to spot unusual activity.
- Vendor Security: Ensure third-party vendors meet strong cybersecurity standards to prevent breaches through external access.
- Collaborate: Work with industry groups and government agencies to stay updated on threats and best practices.
By following these steps, healthcare organizations can reduce the risk of breaches and better protect patient data.
https://www.securityweek.com/560000-people-impacted-across-four-healthcare-data-breaches/